The Eruption Ignites
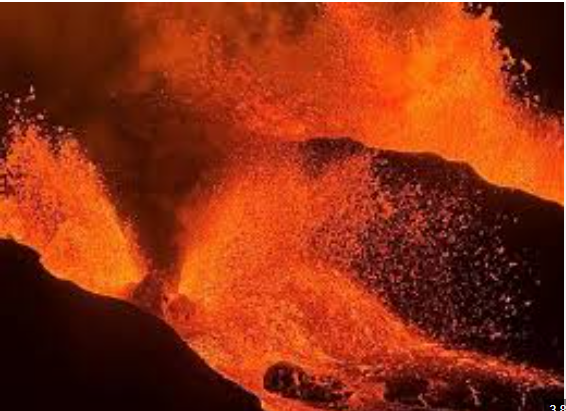
Living near Kīlauea for decades, I’ve learned to read its whispers. On June 28, precursory low-level activity began at 7:27 a.m. with intermittent lava overflows from the north vent. By June 29, sporadic dome fountains evolved into sustained lava fountaining at 9 a.m.—marking the start of episode 27, Hawaii’s 27th eruptive episode since December 23, 2024. The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) confirmed this via Volcanic Activity Notice, noting fountains initially reached 500 feet but soon skyrocketing toward 1,000 feet (305 meters). From my vantage point, the southwest portion of Halemaʻumaʻu Crater glowed like cracked embers, lava streams snaking across the crater floor.
Winds blew northeast to east, per the National Weather Service, but field observations showed variable patterns. This unpredictability risked spreading tephra, vog (volcanic smog), and Pele’s hair downwind across Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park. By 10:30 a.m., U.S. Geological Survey livestreams captured high fountains nearing 1,116 feet—far exceeding early fountain heights. The summit swelled with 16.5 microradians of inflation since June 20, while seismic tremor spiked at 7:30 a.m., triggering rapid escalation.
The Eruption’s Peak and Pause
Volcanic gas emissions surged as sulfur dioxide hit 50,000 tonnes/day, lifting the volcanic cloud height to 11,500 feet. The eruptive plume later peaked at 20,000 feet (6,000 meters), posing general hazards like ashfall and small volcanic particles. By 8 p.m. on June 29, 11 hours of vigorous activity ceased. Lava geysers from the north vent waned, stopping completely at 7:54 p.m., while flames flickered briefly at the south vent. The Uēkahuna tiltmeter (UWD) recorded 16.4 microradians of deflation, coinciding with fading seismic tremor intensity.

Credit photo spectrumlocalnews.com/
This episode produced 1.6 billion gallons of lava, covering 80% of the crater floor. Now cooling within Kaluapele (Kīlauea’s summit caldera), lava flows may show slow movement or incandescence as they solidify. HVO maintains monitoring via livestream cameras, with daily updates on their website. Volcano Alert Level remains WATCH, and Aviation Color Code ORANGE. Crucially, no changes hit the East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone.
Behind the Science
As a volcanologist, I watch Uēkahuna’s tiltmeter like a heartbeat. Inflationary tilt of 15.5 microradians preceded this episode, contrasting Episode 26’s 18.5 microradians of deflationary tilt. Halemaʻumaʻu crater’s rhythm holds true: most eruptive episodes last under a day, followed by pauses of several days. HVO issues VAN/VONA alerts for precursory activity or new episodes, coordinating with Hawai‘i County Civil Defense on hazards. Visitor information is available via Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park’s resources.